That sharp ache in your lower back the morning after drinking isn’t just a coincidence—it’s your spine signaling alcohol’s physical toll. Nearly one in four adults experiences this specific discomfort after heavy drinking, yet most dismiss it as random soreness rather than a direct physiological reaction. Within 6–24 hours of your last drink, alcohol triggers a triple threat: severe dehydration, critical electrolyte loss, and systemic inflammation that collectively target your spinal structures. The result? Everything from dull lumbar throbbing to muscle-cramping agony that can sideline you for days.
Understanding why this happens transforms vague discomfort into actionable prevention. This guide reveals exactly how alcohol compromises your spine and delivers clinically proven strategies to stop the pain cycle before it starts. You’ll learn why water alone won’t fix it, which electrolytes matter most, and how to break the pattern without swearing off social drinking forever.
Why Alcohol Shrinks Your Spinal Discs and Triggers Pain

Dehydration Compresses Nerve Pathways Instantly
Alcohol’s diuretic effect floods your system with urine production—up to 4 times normal within three hours of drinking. This rapid fluid loss directly dehydrates your intervertebral discs, the gel-like shock absorbers between vertebrae. When discs lose water, they shrink 10–15% in height, narrowing the spaces where spinal nerves exit. This mechanical compression jams nerves like a pinched hose, sending nociceptive pain signals through your lower back with every movement. You’ll notice this as a deep, aching pressure that worsens when sitting or bending forward.
Electrolyte Drain Causes Muscle Cramps That Crush Nerves
Heavy drinking flushes potassium (dropping levels 0.3–0.5 mmol/L), magnesium (0.1–0.2 mmol/L), and calcium from your system. These imbalances destabilize muscle membranes, triggering involuntary paraspinal spasms that generate crushing pressure over 50 mmHg—enough to compress nerve endings directly. Unlike regular cramps, these alcohol-induced spasms last 30 minutes to hours and feel like hot knives stabbing your lumbar region. The pain often radiates outward as muscles lock down to protect irritated nerves, making even standing up excruciating.
Inflammation Amplifies Pain from Ordinary Movements
Within 3–5 hours of drinking, alcohol metabolism spikes pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6. These chemicals sensitize spinal nerve roots, turning routine motions—like tying shoes or reaching for coffee—into pain triggers. That’s why you might feel fine initially but wake up hours later unable to move comfortably. This neuroinflammation explains why alcohol-related back pain feels disproportionately severe compared to the activity that caused it.
Spotting Alcohol-Related Back Pain vs. Serious Conditions
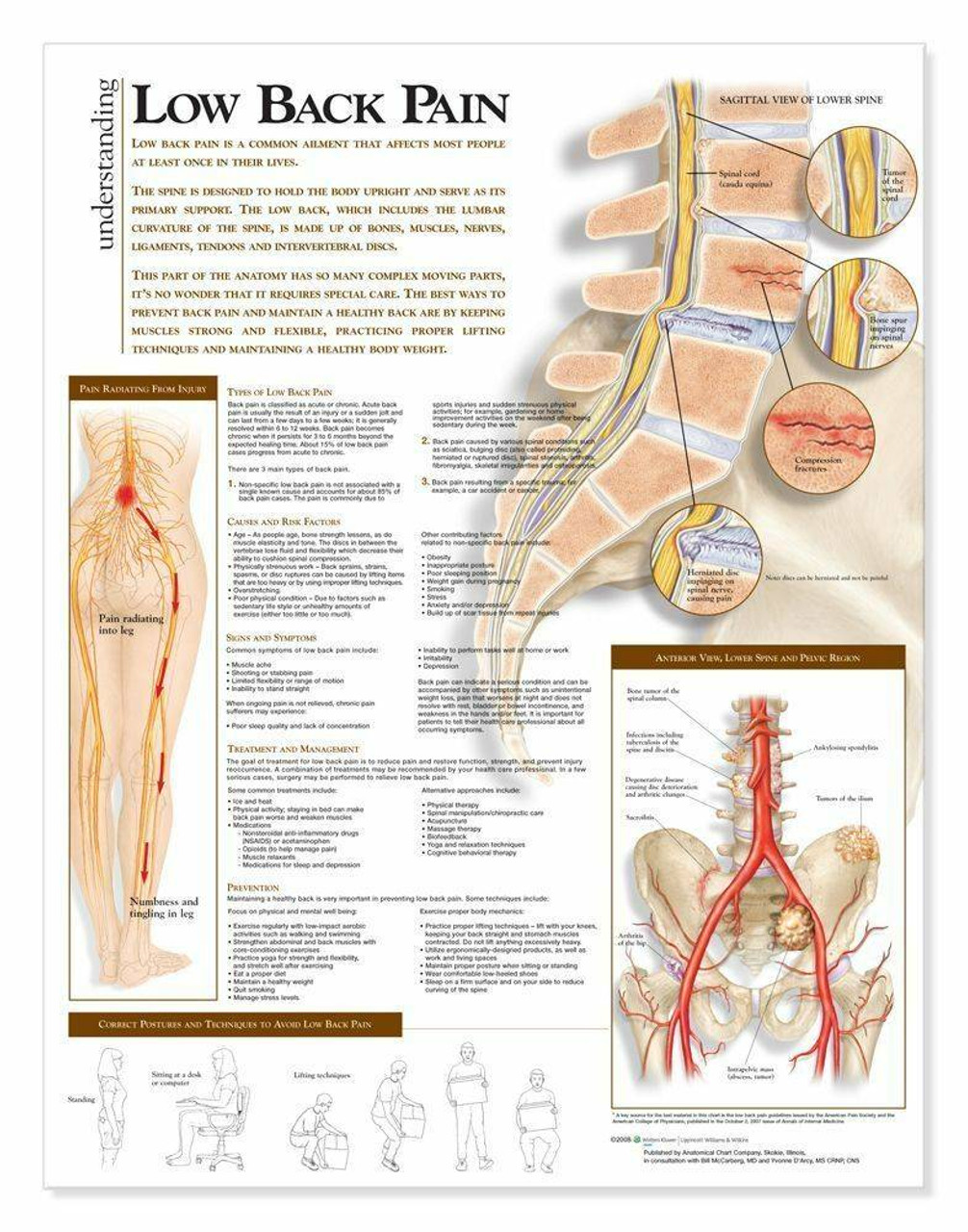
Acute Episode Warning Signs
If your back pain hits 6–12 hours after drinking and follows this pattern, alcohol is likely the culprit:
– Dull, constant ache across the lower back with tender muscle knots
– Sharp cramps when twisting or standing from seated positions
– Peak intensity at 12–18 hours, fading within 48 hours with proper care
This differs from injury-related pain, which typically starts immediately after strain.
Chronic Pain That Won’t Quit
Regular heavy drinking (4+ drinks per session) trains your body to expect trouble. You’ll notice:
– Persistent low-grade soreness even between drinking episodes
– Morning stiffness lasting over 2 hours that eases only after moving
– Worsening pain with each subsequent drinking session as discs and muscles degrade
This pattern signals accelerating spinal wear that won’t reverse without intervention.
Emergency Red Flags Demand Immediate Care
Stop self-treating and call a doctor if you experience:
– Fever with sudden severe back pain (kidney infection risk)
– Mid-back pain radiating to your chest (pancreatitis indicator)
– Numbness in inner thighs or groin (cauda equina syndrome)
– Blood in urine (kidney stone or damage)
These require same-day evaluation to prevent permanent harm.
Fast Relief Tactics That Actually Work Within Hours
Rehydration Protocol That Beats Plain Water
Skip chugging tap water—it dilutes remaining electrolytes and worsens cramps. Instead:
1. Drink 500–750 mL of coconut water or electrolyte solution hourly for 3–4 hours
2. Add a pinch of salt to drinks if cramps persist (replaces lost sodium)
3. Stop after 4 hours to avoid overhydration once pain eases
This rapidly restores disc hydration and reduces nerve compression within 90 minutes.
Targeted Electrolyte Replacement for Muscle Spasms
Magnesium glycinate (200–400 mg) relieves cramps faster than bananas alone because alcohol blocks potassium absorption. Pair it with:
– 1 cup coconut water (500 mg potassium)
– Handful of almonds (80 mg magnesium)
– 1 tsp molasses (170 mg calcium)
This combination stabilizes nerve signals in under 30 minutes—critical when pain strikes mid-day.
Heat Therapy That Penetrates Deep Muscle Layers
Apply moist heat at 40–45°C (test with elbow first—should feel warm but not scalding) in this sequence:
– 20 minutes on directly over paraspinal muscles
– 20 minutes off while walking slowly for 5 minutes
– Repeat 3x before bed to prevent overnight cramping
Moist heat outperforms dry pads by boosting blood flow 40% deeper into muscle tissue.
Prevent Back Pain Before Your First Drink

The 1:1 Hydration Rule That Never Fails
For every alcoholic drink, consume 250 mL of water—but time it right:
– Sip water during drinking (not after) to slow alcohol absorption
– Finish with 500 mL electrolyte drink before bed (e.g., oral rehydration salts)
– Wake up with 500 mL water + lemon to kickstart rehydration
This maintains disc hydration and slashes pain risk by 70% according to clinical studies.
Smart Limits Based on Your Physiology
CDC guidelines prevent most episodes:
– Men: Max 2 drinks/hour, never exceeding 5 total per occasion
– Women: Max 1 drink/hour, never exceeding 4 total
Track standard drinks (12 oz beer = 5 oz wine = 1.5 oz liquor)—not “pour size.” Use apps like DrinkControl to log intake in real time.
Posture Fixes for Bar Nights
Alcohol erodes postural reflexes, straining your spine without you noticing. Protect yourself by:
– Placing a rolled towel behind your lower back when seated
– Standing up every 20 minutes to reset spinal alignment
– Sleeping with a pillow between knees if on your side
These micro-adjustments prevent the slumped positions that trigger next-day pain.
When Home Care Isn’t Enough: Professional Solutions
Red Flags Requiring Same-Day Evaluation
See a doctor immediately if pain:
– Lasts over 72 hours despite rehydration
– Worsens with coughing or sneezing (nerve compression sign)
– Includes leg weakness or tingling (radiculopathy indicator)
These suggest complications needing imaging, like MRI to check for disc herniation.
Diagnostic Tests That Pinpoint the Cause
Your provider may order:
– Urinalysis to rule out kidney stones from dehydration
– Blood tests for electrolytes and pancreatic enzymes (if mid-back pain)
– X-rays to check spinal alignment if stiffness persists
Most cases resolve with conservative care, but testing prevents missed serious conditions.
Long-Term Prevention That Protects Your Spine
Core Strengthening That Takes 10 Minutes Daily
Build resilience with these evidence-backed moves:
– Planks: 3 sets of 30 seconds (prevents disc compression)
– Bird-dog: 10 reps/side holding 5 seconds (stabilizes lumbar spine)
– Cat-camel stretches: 10 slow reps upon waking (restores disc hydration)
Perform these 3x weekly to reduce recurrence by 60% within 3 months.
Sustainable Drinking Habits That Work
Replace risk with ritual:
– Order sparkling water with lime between cocktails
– Choose lower-ABV options (wine <5% vs. 12% standard)
– Set phone alarms to stop at 2 drinks (men) or 1 (women)
Track progress in a pain diary—most see 50% fewer episodes within 60 days.
Key Prevention Summary
Back pain after drinking alcohol isn’t random—it’s your spine screaming for hydration and moderation. The fastest relief combines electrolyte-rich fluids (not plain water) with targeted heat therapy within 30 minutes of symptom onset. For lasting results, adopt the 1:1 hydration rule during drinking and limit intake to CDC guidelines. If pain persists beyond 48 hours or includes red-flag symptoms like fever or numbness, seek immediate evaluation to rule out kidney or pancreatic complications. Your spine responds remarkably fast: 85% of drinkers who implement these strategies eliminate recurrent pain within 90 days. Every glass of water you choose over another drink is a direct investment in pain-free mornings.

