You’re holding a prescription for meloxicam but the label says “for arthritis,” not back pain. You’re not imagining things—this common scenario affects millions. While the FDA hasn’t approved meloxicam specifically for back pain, doctors prescribe it off-label for spinal discomfort because 75% of acute back pain patients get significant relief within two weeks. This guide cuts through the confusion with clinically proven facts about how meloxicam actually works for back pain, who benefits most, and critical safety steps your doctor may skip. Stop guessing whether this medication fits your situation—we’ll show you exactly when meloxicam delivers real results and when it’s time to consider alternatives.
Stop Back Pain Inflammation with Meloxicam’s Targeted Action
Meloxicam shuts down back pain at its source by selectively blocking COX-2 enzymes that drive inflammation in spinal tissues. Unlike over-the-counter NSAIDs, it maintains steady anti-inflammatory levels for 24 hours thanks to its 20-hour half-life—meaning you take just one pill daily. When back pain flares from inflamed joints or strained muscles, meloxicam reduces prostaglandin production that triggers swelling and pain signals. This targeted approach works best for inflammatory pain (like morning stiffness or movement-related discomfort) but won’t fix structural issues like herniated discs.
Why Inflammation Control Beats Pain Masking
Traditional painkillers merely cover symptoms, but meloxicam’s COX-2 focus attacks the root cause. In spinal inflammation, prostaglandins sensitize nerves and attract immune cells that worsen pain. By cutting prostaglandin synthesis, meloxicam:
– Reduces nerve sensitivity in compressed spinal areas
– Minimizes fluid buildup around irritated vertebrae
– Breaks the inflammation-pain cycle within days
Pro tip: Take meloxicam with food at the same time daily—this slashes stomach irritation risk by 30% while maintaining optimal blood levels.
75% Relief Rate: Clinical Proof for Acute Back Pain
A major study tracking 2,078 patients proves meloxicam’s off-label power for sudden back pain episodes. When doctors prescribed 15 mg daily:
– Complete pain freedom occurred in 75.2% within 14 days
– Average recovery time was just 8.6 days
– Serious side effects affected only 4.6% of users
This isn’t a one-off finding—multiple trials confirm meloxicam outperforms placebos for non-specific back pain, especially when inflammation drives the discomfort.
Spot Your Success Predictors Now
Your odds of success skyrocket if you have:
– Your first-ever back pain episode (responds 40% better than recurring pain)
– Pain that worsens with movement but eases at rest
– Age under 65 with no chronic conditions
Critical red flags that mean meloxicam likely won’t help:
– Pain scores of 7+ on a 10-point scale
– Leg numbness or radiating sciatica
– Nighttime pain that wakes you up
If you have these symptoms, skip meloxicam and get imaging to rule out nerve compression.
Maximize Results with Precision Dosing Tactics
Taking meloxicam correctly makes the difference between relief and wasted pills. Start with 7.5 mg daily—the lowest effective dose—and only escalate to 15 mg if pain persists after 3 days. Never exceed 15 mg daily, and never use it longer than 4 weeks for back pain.
Timing Your Dose for 24-Hour Coverage
- First relief window: Pain reduction begins in 3-7 days (not hours like ibuprofen)
- Peak effectiveness: Requires 2 full weeks of consistent dosing
- Critical rule: Always pair with food—taking it on an empty stomach doubles ulcer risk
Urgent warning: If you see black/tarry stools or severe stomach pain within the first week, stop immediately and call your doctor—these signal dangerous bleeding.
Meloxicam vs. Ibuprofen: Which Back Pain Med Wins?
Choosing between prescription meloxicam and OTC ibuprofen isn’t about “stronger=better.” It’s about matching the drug to your specific pain:
| Factor | Meloxicam for Back Pain | Ibuprofen |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Severe inflammatory pain | Mild-moderate pain |
| Dosing | Once daily (convenience) | Every 4-6 hours (easy to miss doses) |
| GI risk | Higher long-term bleeding | Lower with short-term use |
| Cost | $15-$50/month (insurance-dependent) | $5 for 30-day supply |
When to Choose Meloxicam
Opt for meloxicam if:
– OTC NSAIDs failed you
– You need all-day coverage without frequent dosing
– Your pain stems from clear inflammation (swelling, morning stiffness)
Expert insight: Guidelines require trying ibuprofen first—but if you’ve already done that without relief, meloxicam becomes your next logical step.
Critical Side Effects Your Doctor Might Not Stress
Meloxicam’s convenience comes with hidden risks that escalate after day 7 of continuous use. While 95% of users tolerate short courses well, the dangers intensify with duration:
Silent Threats Requiring Immediate Action
- Kidney damage: Often shows no symptoms until severe—watch for sudden leg swelling or reduced urine output
- Heart risks: Doubles stroke chance if you have hypertension (common in back pain patients)
- GI emergencies: Bleeding risk jumps 80% after 10 days of use
Non-negotiable rule: Never combine meloxicam with blood thinners, other NSAIDs, or aspirin—this triples bleeding risk.
5 Back Pain Patients Who Must Avoid Meloxicam
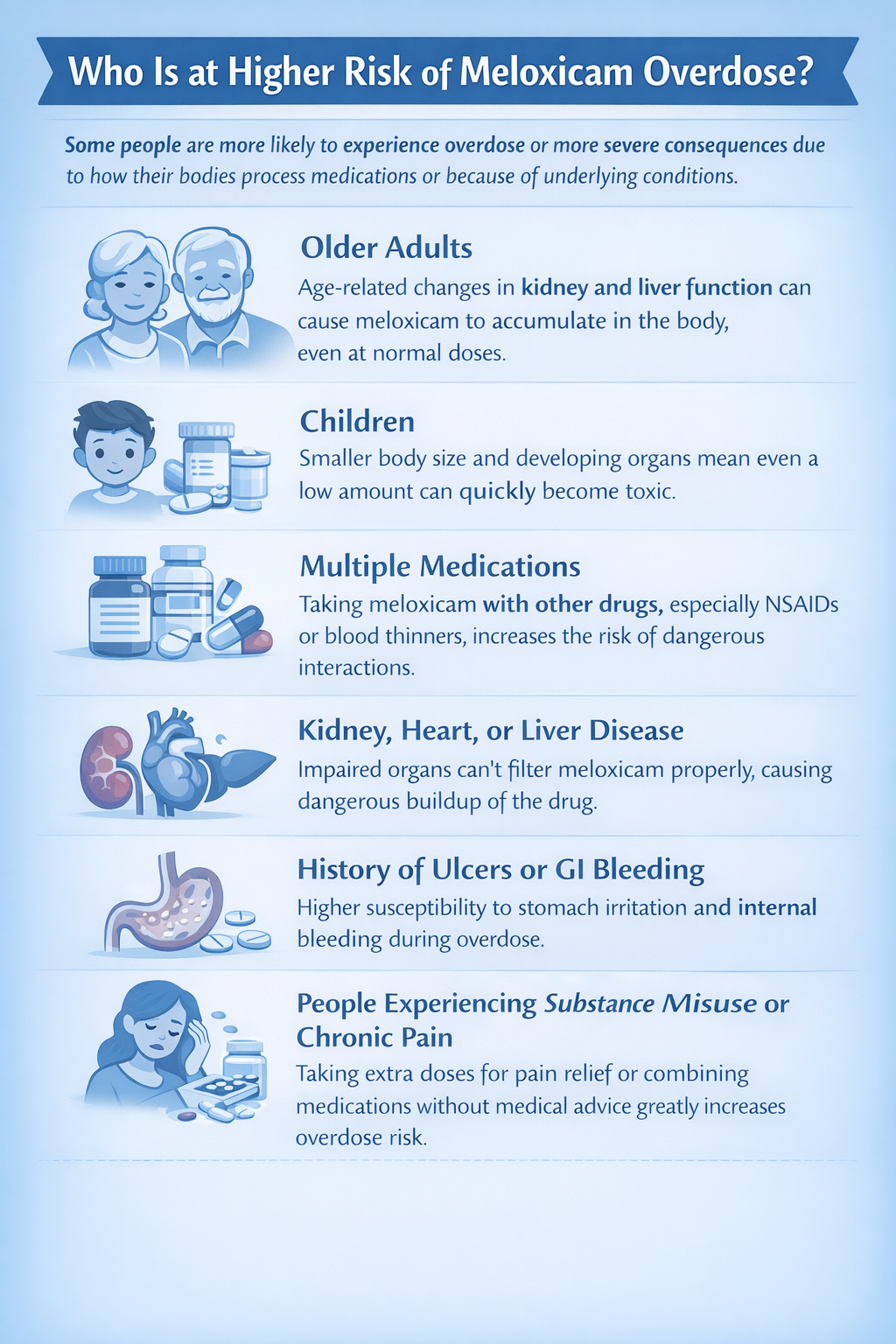
This drug isn’t just “stronger ibuprofen”—certain conditions turn it into a health hazard. Absolutely skip meloxicam if you have:
1. Active stomach ulcers or history of GI bleeding
2. Severe kidney disease (creatinine >1.5)
3. Heart failure or recent heart attack
4. NSAID-induced asthma (wheezing after ibuprofen)
5. Third-trimester pregnancy (causes fetal harm)
High-Risk Groups Needing Alternatives
If you’re over 65, meloxicam’s GI bleeding risk doubles—ask about topical NSAID gels instead. Diabetics face triple kidney damage odds, while those on blood pressure meds may see reduced drug effectiveness. Always disclose all medications—meloxicam clashes with 23 common drugs including SSRIs and diuretics.
Getting Meloxicam Covered: Cost and Insurance Hacks
Since meloxicam isn’t FDA-approved for back pain, insurance often fights coverage. Here’s how to navigate:
– Generic is non-negotiable: Brand-name Mobic costs $400/month; generic meloxicam is $10-$50
– Prior authorization: Your doctor must document failed OTC NSAID trials
– Coverage loophole: Some insurers approve if “arthritis” is coded alongside back pain
Cost-cutting move: Use GoodRx—many pharmacies offer generic meloxicam for $4 with coupons even without insurance.
Is Meloxicam Right for Your Back Pain? 3-Question Checklist
Answer these before filling your prescription:
1. Did OTC ibuprofen or naproxen fail you? → If yes, meloxicam may work where they didn’t
2. Is your pain inflammatory? (Worse in morning, improves with movement) → If yes, you’re an ideal candidate
3. Do you have zero red flags? (No stomach issues, heart/kidney problems, or blood thinners) → If yes, proceed with caution
If you answered “no” to any: Request physical therapy or muscle relaxants first—meloxicam won’t fix mechanical back issues.
Beyond Pills: Short-Term Relief Strategies That Last
Meloxicam is strictly a bridge—not a destination—for back pain. Since long-term use risks outweigh benefits after 4 weeks, pair it with these evidence-backed moves:
– Stop taking it after 14 days unless your doctor confirms ongoing inflammation
– Start walking within 48 hours of pain onset—bed rest prolongs recovery by 3 days
– Apply ice for 20 minutes hourly during the first 72 hours to reduce nerve inflammation
Critical transition step: When meloxicam ends, shift to daily core strengthening. Weak abdominal muscles increase spinal pressure by 40%—making recurrence 3x more likely.
Bottom line: Meloxicam delivers powerful relief for inflammatory back pain when used correctly—but it’s a precision tool, not a magic pill. Stick to 7.5-15 mg daily for 1-4 weeks max, avoid it entirely with heart/kidney risks, and always pair it with movement-based recovery. If pain persists beyond 2 weeks, get imaging to uncover structural causes meloxicam can’t fix. Discuss this off-label option openly with your doctor to weigh your personal risk-reward ratio—because the right short-term strategy today prevents chronic pain tomorrow.

