That sharp ache under your right ribs that worsens when you breathe deeply isn’t just muscle strain—it could signal anything from a simple muscle pull to gallstones. Right side back pain beneath the ribs affects millions annually, yet many suffer in silence, unsure whether to tough it out or rush to the ER. This guide breaks down exactly what your body might be telling you, from harmless muscle tweaks to red-flag emergencies demanding immediate care.
Pinpointing Your Pain Source: Muscle vs. Organ
How to Tell Muscle Strain from Organ Trouble
You’ll know muscle pain when it flares during specific movements like twisting to reach your back seat or after heavy lifting. This type of discomfort typically eases with rest and feels tender when you press the area. Unlike organ-related pain, muscle strain stays localized and often feels like a knot that tightens with certain motions.
Organ pain behaves differently—it may start dull then become sharp, radiate to other areas, and persist regardless of position changes. Gallbladder issues often send pain toward your right shoulder, while kidney problems might travel downward toward your groin. Key differentiator: If pain worsens after eating fatty foods or comes in severe waves, organ involvement is likely.
Rib Injury Warning Signs You Can’t Ignore
Check for these critical indicators if you suspect a rib fracture:
– Exact point tenderness: Pain concentrates precisely where you press
– Breathing complications: Sharp pain intensifies with each inhale
– Bruising development: Discoloration appears within hours of injury
– Abnormal sensations: Grating feeling when touching the area
Most minor rib injuries heal within 4-6 weeks with rest, but complications like punctured lungs require immediate medical attention. Critical warning: If you feel short of breath along with rib pain, seek emergency care immediately.
Costochondritis: The Mimic That Tricks Doctors
This rib cartilage inflammation often gets mistaken for heart or lung issues. You’ll recognize it when pressing on your chest wall triggers the same pain you feel in your back. Deep breaths become painful events, yet you won’t have fever, cough, or other systemic symptoms. Costochondritis typically follows intense coughing spells or heavy lifting sessions and can last weeks to months.
Gallbladder Crisis: Recognizing the Emergency Signs
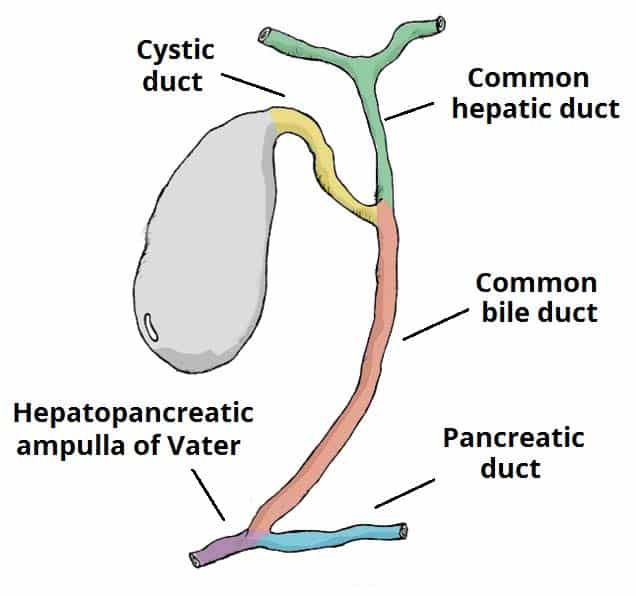
Acute Cholecystitis vs. Gallstone Attacks
Acute cholecystitis feels like pressure building under your ribs that won’t let up. The pain intensifies gradually, often accompanied by fever and persistent nausea. Gallstone attacks strike in waves—severe cramping that peaks then subsides, typically 30-60 minutes after eating fatty foods.
Watch for these critical gallbladder danger signs:
– Fever exceeding 101°F with chills
– Uncontrolled vomiting that won’t stop
– Yellowing of skin or eyes (jaundice)
– Clay-colored stools indicating bile obstruction
Meal Timing Clues to Your Pain Source
Track when your pain strikes relative to eating. If that cheeseburger triggered a two-hour ache under your ribs, your gallbladder is likely signaling trouble. Gallbladder pain typically:
– Starts 30-60 minutes post-meal as bile release moves stones
– Worsens at night when bile concentration peaks during fasting
– Radiates to your right shoulder through nerve referral patterns
– Increases with fatty foods that demand maximum bile production
Kidney Stone Pain: From Dull Ache to Emergency
The Pain Progression You Must Recognize
Kidney stones begin as vague discomfort under your ribs before escalating dramatically. The pain journey follows this pattern:
1. Initial stage: Mild ache in upper back near lower ribs
2. Escalation: Severe pain radiating toward groin area
3. Colicky waves: Intense pain cycles lasting 20-60 minutes
4. Systemic symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and urinary urgency
Critical distinction: Kidney stone pain typically comes in waves, while blocked kidney drainage (hydronephrosis) creates constant, dull ache with visible flank swelling and urinary changes. Fever with these symptoms indicates dangerous infection requiring immediate antibiotics.
Pulmonary Dangers Hiding as Back Pain
Right lower lobe pneumonia causes back pain that worsens with breathing, accompanied by productive cough with colored mucus, fever, and shortness of breath during mild activity. Pleurisy presents as knife-like pain with each breath, often following a viral illness.
Life-threatening emergency: Pulmonary embolism demands immediate 911 response when you experience sudden sharp chest pain under ribs, inability to catch your breath even at rest, racing heart (over 100 bpm), especially after recent long flights, surgery, or while on birth control pills.
Your Diagnostic Roadmap: Tests That Find the Cause

Why Ultrasound Comes First for Right Side Pain
Your doctor will likely order a right upper quadrant ultrasound first—it rules out 80% of serious causes without radiation exposure. This test effectively evaluates your gallbladder for stones or inflammation, checks liver size and texture, identifies kidney stones or obstructions, and provides immediate visual feedback.
When CT Scans Become Necessary
CT imaging steps in when ultrasound findings are inconclusive or when your symptoms suggest complex issues. Doctors order CT scans to precisely locate kidney stones, evaluate trauma injuries, assess possible abscesses, or investigate confusing symptom combinations. While CT delivers more radiation than ultrasound, its detailed imaging often proves crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Blood Tests That Tell the Full Story
Essential lab work provides critical context about your internal systems:
– Liver function markers (ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase) reveal inflammation
– Kidney indicators (creatinine, BUN) show filtration efficiency
– Infection signs (white blood cell count, CRP) confirm inflammatory response
– Stone risk factors (calcium, uric acid levels) help prevent recurrence
Immediate Relief Strategies You Can Try Tonight
The 72-Hour Home Care Protocol
For musculoskeletal pain, follow this precise timeline:
– First 24 hours: Apply ice 20 minutes on, 20 minutes off—never use heat initially
– Days 2-3: Switch to gentle heat therapy while continuing light movement
– Throughout: Take NSAIDs as directed and avoid aggravating activities
– Critical mistake to avoid: Don’t completely immobilize—gentle walking maintains circulation
Strategic Positioning for Different Pain Types
- Kidney stone sufferers: Curl in fetal position with small pillow supporting ribs
- Gallbladder pain relief: Sit upright and lean slightly forward to reduce pressure
- Muscle strain comfort: Lie on your left side with pillow between knees
- Breathing help: Place hand on painful area while taking slow, shallow breaths
Heat vs. Ice: Which Works for Your Pain
Heat helps chronic muscle tension, arthritis flare-ups, and menstrual-related back pain by increasing blood flow. Ice works better for acute injuries, inflammation, and recent trauma by reducing swelling. Neither provides relief for organ-related pain—these require medical treatment rather than home remedies.
Proven Treatment Paths Based on Your Diagnosis
Gallbladder Surgery Reality Check
If surgery becomes necessary, laparoscopic cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) follows this realistic timeline:
– Hospital stay: Same-day discharge or one overnight stay
– Recovery: Return to desk work in 1-2 weeks, full physical activity in 4-6 weeks
– Diet progression: Clear liquids → low-fat foods → normal diet over 2-4 weeks
– Long-term impact: Most people adapt well without their gallbladder
Kidney Stone Passage Support System
Increase your odds of passing stones naturally:
– Hydration strategy: Drink 2-3 liters daily, mostly water
– Medication aid: Tamsulosin relaxes ureter muscles to ease passage
– Stone capture: Strain urine to catch stones for laboratory analysis
– Pain management: Prescription NSAIDs like Toradol provide targeted relief
Muscle Strain Recovery Timeline
Follow this progressive return-to-activity schedule:
– Week 1: Walking only, gentle stretching, no twisting motions
– Week 2: Light core strengthening exercises, avoid heavy lifting
– Week 3-4: Gradual return to normal activities as tolerated
– Week 6: Full activity resumption if pain-free during movement
Prevention Tactics That Actually Work
Core Strengthening Exercises You Can Do Daily
Build back resilience with these simple moves:
– Bird-dogs: 3 sets of 10 per side, focusing on spinal alignment
– Side planks: Hold 30 seconds, 3 repetitions per side
– Dead bugs: 2 sets of 12 controlled movements, maintaining pelvic stability
– Glute bridges: 2 sets of 15, squeezing at the top for maximum benefit
Gallstone-Preventing Food Swaps
Reduce gallstone risk by 20% with these practical dietary changes:
– Instead of red meat: Choose lean poultry or fish prepared without added fats
– Instead of full-fat dairy: Opt for low-fat alternatives like Greek yogurt
– Instead of fried foods: Select baked, grilled, or steamed cooking methods
– Add daily fiber: Incorporate 25-30g from vegetables and whole grains
Emergency Warning Signs That Demand 911
Absolute Red Flags Requiring Immediate Care
Call emergency services immediately if you experience:
– Severe pain with fever over 101°F indicating possible infection
– Complete inability to keep food or liquids down risking dehydration
– Sudden breathing difficulties or chest pressure symptoms
– Trauma followed by intense pain suggesting internal injury
– Visible blood in urine or stool requiring urgent investigation
Monitoring Protocol for Less Severe Cases
You can safely monitor symptoms for 24-48 hours if:
– Pain responds to over-the-counter medication
– No fever, vomiting, or systemic symptoms develop
– Function gradually improves with rest
– Pain follows predictable patterns matching muscle strain
Right side back pain under ribs rarely resolves with wishful thinking. Whether it’s a strained muscle demanding rest or gallstones requiring medical intervention, understanding your body’s signals empowers better decisions. Track your symptoms carefully, know when to seek help, and remember—persistent pain always deserves professional evaluation. Your ribs protect vital organs for a reason; when they hurt, your body is sending a message worth decoding.